Methyltetrahydrofolate is the active form of folate, essential for DNA synthesis and repair. This nutrient supports heart health and prevents neural tube defects in pregnancy. Learn about its benefits, side effects, and how to use it safely in this guide.
Key Takeaways
Methyltetrahydrofolate is the active form of folate critical for DNA synthesis, amino acid metabolism, and preventing neural tube defects during pregnancy.
Health benefits include supporting cardiovascular health by lowering homocysteine levels and enhancing the efficacy of antidepressants in individuals with depression.
Proper dosage ranges from 400 to 800 mcg for adults, with pregnant women needing up to 600 mcg, and potential side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances and irritability.
Understanding Methyltetrahydrofolate
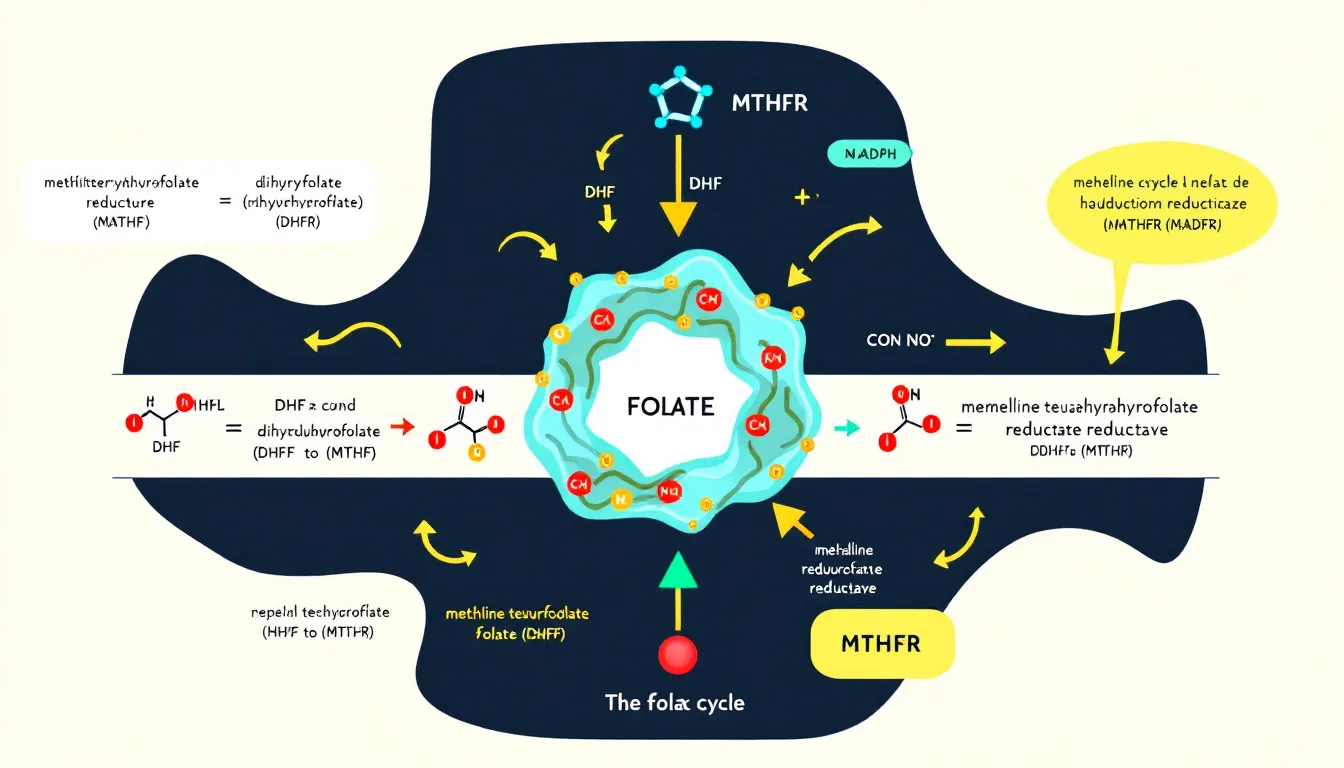
Methyltetrahydrofolate, also known as levomefolic acid, L-5-MTHF, or L-methylfolate, is the active form of folate that our bodies can directly use. Unlike synthetic folic acid, which must be converted into its active form, methyltetrahydrofolate is readily absorbed and utilized by the body. This conversion process primarily occurs in the small intestine and involves the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR).
The significance of methyltetrahydrofolate in human health cannot be overstated. It is essential for DNA synthesis and repair, as well as amino acid metabolism, which are fundamental to cellular function and overall well-being. Moreover, it plays a crucial role in the folate cycle, which is vital for reducing the risk of various health issues such as neural tube defects and cardiovascular diseases.
Understanding the role of methyltetrahydrofolate in folate metabolism helps us appreciate its importance in maintaining optimal health. From preventing folate deficiency to supporting various metabolic processes, methyltetrahydrofolate is a cornerstone of human nutrition.
Health Benefits of Methyltetrahydrofolate

Methyltetrahydrofolate offers numerous health benefits, making it an essential nutrient for everyone. Preventing neural tube defects, supporting cardiovascular health, and enhancing the effects of antidepressants are some of the critical roles methyltetrahydrofolate plays in human nutrition.
Preventing Neural Tube Defects
One of the most crucial roles of methyltetrahydrofolate is in pregnancy, where adequate levels can significantly reduce the risk of neural tube defects in infants. Neural tube defects, such as spina bifida and anencephaly, occur when the spinal cord and brain do not develop properly during early pregnancy. Expectant mothers should ensure adequate intake of methyltetrahydrofolate before and during early pregnancy to decrease the likelihood of these congenital defects.
Women of childbearing age should take folic acid supplements to prevent such birth defects. During pregnancy, a daily intake of 300-600 mcg of folic acid is recommended to help prevent neural tube defects. Proper folate levels help safeguard the health of future generations.
Cardiovascular Health
Another vital role of methyltetrahydrofolate is in cardiovascular health. It helps convert homocysteine to methionine, an amino acid that is crucial for heart health. Elevated homocysteine levels have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, making this conversion process essential.
Lowering homocysteine levels with methyltetrahydrofolate can potentially reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Folate supplementation is often recommended by healthcare professionals as part of a comprehensive approach to heart health, underscoring its importance in human nutrition.
Enhancing Antidepressant Effects
Individuals dealing with depression may find additional benefits from methyltetrahydrofolate. Methyltetrahydrofolate supplementation can enhance the effectiveness of standard antidepressants like SSRIs and SNRIs. Improving neurotransmitter synthesis in the brain, methyltetrahydrofolate can lead to faster symptom relief and better treatment outcomes in major depressive disorder.
Methylation, a critical biochemical process involving 5-MTHF, is essential for the synthesis of amino acids and the regulation of gene expression. This process is essential for maintaining mental health, making methyltetrahydrofolate a valuable addition to traditional antidepressant treatments.
Side Effects and Risks

While methyltetrahydrofolate is generally well-tolerated, it is important to be aware of potential side effects and risks.
Awareness of these can help you use this nutrient safely and effectively.
Common Adverse Effects
Although side effects from methyltetrahydrofolate are typically minimal, some individuals may experience gastrointestinal disturbances, skin rashes, irritability, achy joints, headaches, and fatigue. These symptoms are usually mild and temporary.
A serious allergic reaction to methyltetrahydrofolate is very rare, but if it occurs, immediate medical attention is necessary. If any side effects persist or worsen, it is crucial to seek medical help right away.
Increased Risk Factors
Certain genetic mutations, particularly in the MTHFR gene, increase the likelihood of experiencing adverse effects from methyltetrahydrofolate. People with these genetic variations may be at a greater risk for adverse effects from supplementation. Genetic screening can help identify these risks and guide proper supplementation strategies.
Individuals with the MTHFR gene mutation are at a higher risk for adverse reactions to methyltetrahydrofolate. Working with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the best approach for supplementation if you have a known genetic variation.
Proper Dosage and Administration

Proper dosage and administration are key to maximizing the benefits of methyltetrahydrofolate while minimizing potential risks.
Recommended Dosage
The standard dosage of methyltetrahydrofolate varies based on age, health conditions, and specific dietary needs. Adults usually need between 400 to 800 mcg daily, while pregnant women may require up to 600 mcg. For maximum benefits, take methyltetrahydrofolate consistently at the same time each day, with or without food.
Avoid taking more than 1000 mcg of folic acid daily unless prescribed by a healthcare provider. This helps prevent potential adverse effects and ensures safe supplementation.
Overdose Symptoms
Symptoms of methyltetrahydrofolate overdose can include significant changes in mood and mental state. In case of an overdose, call 911 immediately.
Awareness of these symptoms can help you respond quickly and seek appropriate medical care.
Drug Interactions
Methyltetrahydrofolate can interact with other drugs, altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of severe side effects. Inform your healthcare provider of all medications and dietary supplements you are taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Medical professionals often conduct blood tests to monitor folate and vitamin B-12 levels in patients taking methyltetrahydrofolate. This monitoring helps ensure that the supplementation is effective and safe. Consult your doctor before starting or changing any medications.
Food Sources and Supplements

Methyltetrahydrofolate can be obtained from various natural food sources and supplements. Knowing these sources can help you make informed decisions about your diet and supplementation.
Natural Food Sources
Dark green leafy vegetables, such as spinach and romaine lettuce, are excellent sources of folate. Asparagus, Brussels sprouts, beans, lentils, and chickpeas are also rich in dietary folate. Incorporating these foods into your diet can naturally boost your methyltetrahydrofolate levels.
Citrus fruits and juices are tasty ways to enhance your folate intake. Whole grains, especially fortified foods, are significant sources of folate and are often used in food fortification programs to improve public health.
Folate is essential for DNA synthesis and repair, contributing to overall health and well-being. Including a variety of folate-rich foods in your diet is a natural way to support your health.
Choosing a Supplement
Choose high-quality methyltetrahydrofolate supplements that ensure proper bioavailability. 5-MTHF, a naturally occurring form of folate, is better absorbed than synthetic folic acid, even under altered gastrointestinal conditions. Methylated forms of folate, such as L-methylfolate, offer better absorption.
Check that the supplement is labeled as ‘biologically active’ or ‘bioavailable’ to guarantee better absorption. Ensure the supplement contains a balanced dosage that meets recommended daily allowances without exceeding them.
Select methylfolate supplements with guaranteed potency that are free from common allergens. For better safety, avoid supplements with artificial additives and allergens.
Special Considerations
Certain groups, such as pregnant women and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, may face increased risks when using methyltetrahydrofolate.
These considerations can help ensure safe and effective use.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Folic acid is safe to use during pregnancy. Follow the recommended guidelines. It is also unlikely to harm a nursing infant. This holds true even if it passes into breast milk. Inform your doctor of any allergies, medical history, and all medications before using methyltetrahydrofolate.
Supplementing with natural (6S)-5-methyltetrahydrofolate may prevent the increase of unmetabolized folic acid in breast milk, which is linked to reduced bioavailability for infants. This ensures both mother and infant benefit from the supplementation.
Medical Conditions and Surgery
Individuals with specific medical conditions should consult their healthcare provider about folate supplementation to avoid potential complications. Patients undergoing medical procedures like angioplasty should avoid high doses of folic acid due to potential complications.
Inform your doctor or dentist about all products used before surgery. This disclosure helps ensure your safety during medical procedures.
Summary
In summary, methyltetrahydrofolate plays a vital role in human health, offering numerous benefits, from preventing neural tube defects to enhancing cardiovascular health and supporting mental well-being. Understanding its proper usage, potential side effects, and special considerations can help you make informed decisions about including this nutrient in your diet or supplementation routine.
By incorporating methyltetrahydrofolate into your health regimen, you can take proactive steps towards a healthier, more vibrant life. Always consult with healthcare professionals to tailor your approach to your specific needs and conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is methyltetrahydrofolate?
Methyltetrahydrofolate, or L-methylfolate, is the active form of folate essential for cellular functions such as DNA synthesis and amino acid metabolism. Its absorbable nature makes it crucial for overall health.
How does methyltetrahydrofolate benefit pregnancy?
Methyltetrahydrofolate is essential for pregnancy as it greatly decreases the risk of neural tube defects in infants, including spina bifida and anencephaly. Ensuring sufficient intake before and during early pregnancy is crucial for fetal health.
Can methyltetrahydrofolate help with cardiovascular health?
Methyltetrahydrofolate can indeed benefit cardiovascular health by lowering homocysteine levels, which are linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases. This conversion process helps promote overall heart health.
What are some common side effects of methyltetrahydrofolate?
Common side effects of methyltetrahydrofolate include gastrointestinal disturbances, skin rashes, irritability, achy joints, headaches, and fatigue, which are typically mild and temporary.
How should methyltetrahydrofolate be taken?
Methyltetrahydrofolate should be taken consistently at the same time each day, with or without food. Adults typically take 400 to 800 mcg daily, while pregnant women may require up to 600 mcg.

